Ciliary processes
| Ciliary processes | |
|---|---|
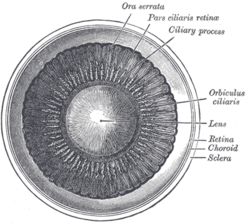 Interior of anterior half of bulb of eye. (Ciliary process visible at upper right.) | |
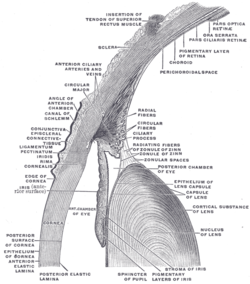 Sagittal diagram of the eye. Ciliary process visible superior to the lens, immediately above the Zonule of Zinn. | |
| Details | |
| Artery | Short posterior ciliary arteries |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | processus ciliares |
| TA98 | A15.2.03.011 |
| TA2 | 6767 |
| FMA | 58486 |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
In the anatomy of the eye, the ciliary processes are formed by the inward folding of the various layers of the choroid, viz. the choroid proper and the lamina basalis, and are received between corresponding foldings of the suspensory ligament of the lens.
Anatomy
They are arranged in a circle, and form a sort of frill behind the iris, around the margin of the lens.
They vary from sixty to eighty in number, lie side by side, and may be divided into large and small; the former are about 2.5 mm. in length, and the latter, consisting of about one-third of the entire number, are situated in spaces between them, but without regular arrangement.
They are attached by their periphery to three or four of the ridges of the orbiculus ciliaris, and are continuous with the layers of the choroid: their opposite extremities are free and rounded, and are directed toward the posterior chamber of the eyeball and circumference of the lens.
In front, they are continuous with the periphery of the iris.
Their posterior surfaces are connected with the suspensory ligament of the lens.
Function
The ciliary processes produce aqueous humour.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1010 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1010 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Histology at une.edu Archived 2013-03-08 at the Wayback Machine
- Histology image: 08011loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/eye/eye.htm#iris
- v
- t
- e
(outer)
| Sclera | |
|---|---|
| Cornea |

tunic (middle)
| Choroid | |
|---|---|
| Ciliary body |
|
| Iris |
| Layers | |
|---|---|
| Cells |
|
| Other |
of the eye
| Anterior segment | |
|---|---|
| Posterior segment |
- Keratocytes
- Ocular immune system
- Optical coherence tomography
- Eye care professional
- Eye disease
- Refractive error
- Accommodation
- Physiological Optics
- Visual perception











