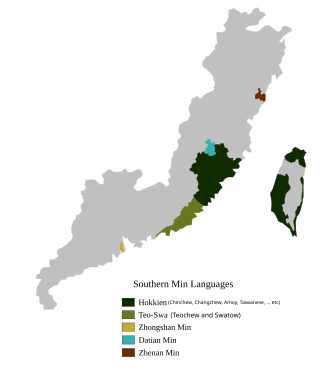
Datian Min
| Datian Min | |
|---|---|
| 大田闽语 / 大田话 | |
| Native to | Southern China |
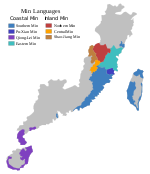
| Region | Datian County, Sanming Prefecture, Fujian |
Native speakers | 250,000 (2012)[1] |
Language family | Sino-Tibetan
|
Early forms | Proto-Sino-Tibetan
|
Writing system | Chinese characters, Peh-oe-ji |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | None (mis) |
| Glottolog | dati1239 |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-ja |
 Datian Min | |
Datian Min (simplified Chinese: 大田闽语; traditional Chinese: 大田閩語; pinyin: Dàtián Mǐnyǔ; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Tāi-chhân bân-gú or simplified Chinese: 大田话; traditional Chinese: 大田話; pinyin: Dàtiánhuà 'Datian speech') is a Southern Min language spoken in Datian County, Sanming City, Fujian Province, China. It has been influenced by other Min languages, including Central Min, Eastern Min, Northern Min and Puxian Min.
Datian Min developed from Hokkien, a dialect of Southern Min. Before the year 1535, this area belonged to four counties: Youxi, Dehua, Yong'an and Zhangping. Hokkien was spoken in Dehua and Zhangping, while Yong'an and Youxi spoke Central Min and Eastern Min respectively. Datian County was set up and affiliated to Yanping Fu (延平府, modern Nanping) which spoke Northern Min in 1535. Language contact occurred in the later days. The county changed affiliate to Yongchun Zhou (永春州, modern Yongchun County, spoke Hokkien dialect) in 1734, then to Yong'an Division (永安专区, modern Sanming Prefecture, spoke Central Min) in 1949. The administrative here changed so frequently that the differences between Datian Min and Hokkien dialect became more and more obvious.
Datian Min has little intelligibility with other varieties of Southern Min, and is sometimes classified as a separate branch of Min. Some Chinese scholars call it Min dialects transition area (闽方言过渡区).
Notes
References
- ^ Zhou, Changji (2012). "B2-5 Fújiàn Shěng de Hànyǔ fāngyán" B2—5 福建省的汉语方言. Zhōngguó yǔyán dìtú jí 中国语言地图集 [Language Atlas of China] (in Chinese). Vol. 汉语方言卷 (2nd ed.). Beijing: Commercial Press. pp. 177–180. ISBN 978-7-100-07054-6.
- ^ Mei, Tsu-lin (1970), "Tones and prosody in Middle Chinese and the origin of the rising tone", Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, 30: 86–110, doi:10.2307/2718766, JSTOR 2718766
- ^ Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1984), Middle Chinese: A study in Historical Phonology, Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press, p. 3, ISBN 978-0-7748-0192-8
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (2023-07-10). "Glottolog 4.8 - Min". Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. doi:10.5281/zenodo.7398962. Archived from the original on 2023-10-13. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- v
- t
- e
Languages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||
Research | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
 | This Sino-Tibetan languages-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e