| RGS6 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | RGS6, GAP, regulator of G-protein signaling 6, regulator of G protein signaling 6, HA117, S914 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 603894; MGI: 1354730; HomoloGene: 68385; GeneCards: RGS6; OMA:RGS6 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 14 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 14q24.2 | Start | 71,932,439 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 72,566,529 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 12 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 12 D1|12 38.14 cM | Start | 82,635,066 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 83,208,830 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - sural nerve
- middle temporal gyrus
- Achilles tendon
- prefrontal cortex
- testicle
- right frontal lobe
- primary visual cortex
- Brodmann area 23
- apex of heart
- buccal mucosa cell
|
| | Top expressed in | - facial motor nucleus
- superior frontal gyrus
- neural layer of retina
- primary visual cortex
- dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation granule cell
- cerebellar cortex
- aortic valve
- atrium
- embryo
- right kidney
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 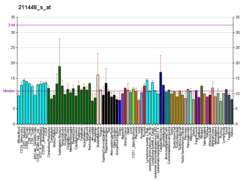

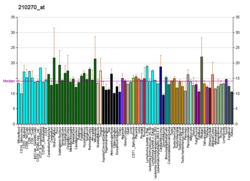 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- GTPase activator activity
- GTPase activity
| | Cellular component | - cytosol
- plasma membrane
- membrane
- nucleus
- extrinsic component of membrane
- cytoplasm
- intracellular anatomical structure
| | Biological process | - G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of GTPase activity
- negative regulation of signal transduction
- intracellular signal transduction
- regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001204416
NM_001204417
NM_001204418
NM_001204419
NM_001204420
|
|---|
NM_001204421
NM_001204422
NM_001204423
NM_001204424
NM_004296 |
| |
|---|
NM_001282061
NM_015812
NM_001310478 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001191345
NP_001191346
NP_001191347
NP_001191348
NP_001191349
|
|---|
NP_001191350
NP_001191351
NP_001191352
NP_001191353
NP_004287
NP_001357199
NP_001357200
NP_001357201
NP_001357202
NP_001357203
NP_001357204
NP_001357205
NP_001357206
NP_001357207
NP_001357208
NP_001357209
NP_001357210
NP_001357211
NP_001357212
NP_001357213
NP_001357215
NP_001357216
NP_001357217
NP_001357218
NP_001357219
NP_001357220
NP_001357221
NP_001357222
NP_001357223 |
| |
|---|
NP_001268990
NP_001297407
NP_056627 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 14: 71.93 – 72.57 Mb | Chr 12: 82.64 – 83.21 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

 2es0: Structure of the regulator of G-protein signaling domain of RGS6
2es0: Structure of the regulator of G-protein signaling domain of RGS6






















