Western heather vole
| Western heather vole | |
|---|---|
 | |
Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Cricetidae |
| Subfamily: | Arvicolinae |
| Genus: | Phenacomys |
| Species: | P. intermedius |
| Binomial name | |
| Phenacomys intermedius (Merriam, 1889) | |
 | |
The western heather vole (Phenacomys intermedius) is a small vole found in western North America. Until recently, the eastern heather vole, (Phenacomys ungava), was considered to be a subspecies. They have short ears with stiff orange hair inside and a short thin tail which is paler underneath. Their long soft fur is brownish with silver grey underparts. They are roughly 14 cm (5.5 in) long with a tail length shorter than one-half their body length, approximately 50 mm (2.0 in). They weigh about 40 g (1.4 oz).[2]
Distribution and habitat
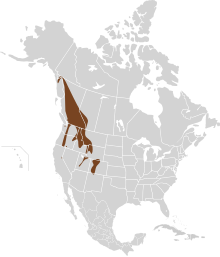
Western heather voles are found in alpine meadows, open shrubby areas, dry forests with shrubs below to provide cover and tundra regions, usually near water, in British Columbia, the Yukon and the western United States.[3]
In summer, they live in burrows where they make nests of grasses and small foliage. These nests are usually near the surface, above 20 cm from the ground, and after often underneath objects such as rocks and logs. In winter, they tunnel under the snow. They store food for later use year-round.[2]
Behavior and ecology
They feed on plant leaves and berries in summer and plant bark and buds in winter, also seeds and fungi. Predators include owls, hawks and carnivorous mammals.[3]
They are active year-round, and are crepuscular, being more active at twilight and at night than during the day.[4]
When captured, western heather vole are docile and non-aggressive, though are generally more aggressive during breeding season.[4]
Reproduction
The female vole has 2 or 3 litters of 2 to 9 young in a nest made from grasses. Aside from western heather voles that live in high-elevations, which may exhibit shorter breeding seasons, their standard breeding season is from May to August. Both male and females are mature after one year and have a lifespan of 4 years or less.[2]
Population
The population of this animal has been reduced in some parts of its range because of clearcutting of forests. As also seen in other high-elevation populations, climate change and the resulting melting of ice sheets in habitats previously inhabited by western heather vole have caused the population and differentiation of populations within the species to decrease. Some populations have also migrated north due to global warming,[5] as during the Last Glacian Maximum, western heather voles have populations much farther south than they are currently, some as far south as Tennessee and Arkansas.[3]
References
- ^ Cassola, F. (2017) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Phenacomys intermedius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T42636A115197827. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T42636A22389824.en. Retrieved 28 November 2022. Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of least concern.
- ^ a b c McAllister, James A.; Hoffmann, Robert S. (1988). "Phenacomys intermedius". Mammalian Species (305): 1–8. doi:10.2307/3504242. ISSN 0076-3519. JSTOR 3504242.
- ^ a b c "Heather vole | Explore the Ice Age Midwest". Illinois State Museum. Retrieved 2022-10-13.
- ^ a b Smith, Donald; Foster, Bristol (1957). "Notes on the Small Mammals of Churchill, Manitoba". Journal of Mammalogy. 38 (1): 98–115. doi:10.2307/1376480. JSTOR 1376480.
- ^ Chavez, Andreas S.; Kenagy, G. J. (16 August 2010). "Historical biogeography of western heather voles (Phenacomys intermedius) in montane systems of the Pacific Northwest". Journal of Mammalogy. 91 (4): 874–885. doi:10.1644/09-MAMM-A-303.1. S2CID 55692333.
- v
- t
- e
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Infraclass: Eutheria
- Superorder: Euarchontoglires
- Order: Rodentia
- Family: Cricetidae
| Arvicola (Water voles) |
|
|---|
| Alexandromys |
|
|---|---|
| Chionomys (Snow voles) |
|
| Hyperacrius (Voles from Pakistan) |
|
| Lasiopodomys |
|
| Lemmiscus |
|
| Microtus (Voles) |
|
| Neodon (Mountain voles) |
|
| Proedromys |
|
| Stenocranius |
|
| Volemys |
|
(Collared lemmings)
| Dicrostonyx |
|
|---|
(mole voles)
| Ellobius (Mole voles) |
|
|---|
(Steppe lemmings)
| Eolagurus |
|
|---|---|
| Lagurus |
|
(Lemmings)
| Lemmus (True lemmings) |
|
|---|---|
| Myopus |
|
| Synaptomys (Bog lemmings) |
|
| Alticola (Voles from Central Asia) |
|
|---|---|
| Caryomys |
|
| Eothenomys (Voles from East Asia) |
|
| Clethrionomys (some Red-backed voles) |
|
| Craseomys (other Red-backed voles) |
|
| Neofiber |
|
|---|---|
| Ondatra |
|
| Dinaromys |
|
|---|
| Arborimus (Tree voles) |
|
|---|---|
| Phenacomys (Heather voles) |
|
| Prometheomys |
|
|---|










