Récepteur du facteur de croissance épidermique
| EGFR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | EGFR, Récepteur du facteur de croissance épidermique, Récepteur de l'EGF | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IDs externes | OMIM: 131550 MGI: 95294 HomoloGene: 74545 GeneCards: EGFR | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
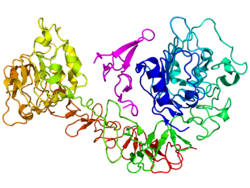
Le récepteur du facteur de croissance épidermique, récepteur de l'EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor) ou EGFR est une protéine dimérique transmembranaire elle est composée de deux monomères (composés de deux sous unités alpha/Beta). La sous unité alpha va permettre la réception de l'EGF et la sous unité Beta va permettre la phosphorylation croisée. Cette protéine transduit le signal consécutif à sa liaison au facteur de croissance épidermique. C'est une protéine à activité tyrosine kinase intrinsèque. Il présente des similitudes avec le récepteur de l'insuline. Il appartient à la famille RTK des récepteurs à activité tyrosine kinase. Son gène est le EGFR porté par le chromosome 7 humain.
Pathologie
Les mutations de ce récepteur dans les cellules non somatiques sont associées à plusieurs formes de cancer, en particulier celui du sein et du poumon[5].
Principales mutations
- Exon 19 : délétions (sensibilité aux inhibiteurs des tyrosines kinases - TKI)
- Exon 20 : insertions, T790M, qui est une cause de la résistance au traitement[6].
- Exon 21 : L858R
Thérapeutique ciblée
Des anticorps monoclonaux ciblant le récepteur de l'EGF [7](cétuximab, panitumumab et matuzumab) ou des petites molécules (inhibiteurs des tyrosines kinases tel que le géfitinib, erlotinib, afatinib, osimertinib et rociletinib) sont utilisés dans le traitement de certains cancers.
Notes et références
- ↑ a b et c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000146648 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ a b et c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020122 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour l'Homme », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour la Souris », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA, Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer, Nat Rev Cancer, 2007;7:169-181
- ↑ Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors, Sci Transl Med, 2011;3:75ra26-75ra26
- ↑ Les thérapies ciblées Gaëtan des Guetz et Jean-Yves Blay Springer 2008
Liens externes
- Ressource relative à la santé
 :
: - Medical Subject Headings
v · m | |
|---|---|
| Ligand | |
| Récepteur |
|
| Autres | |
 Portail de la biochimie
Portail de la biochimie